Effective Tips for Treating Stomatitis and Mouth Sores
Mouth sores and stomatitis can affect people of all ages, from children to adults. They can be caused by various factors such as infections, poor oral hygiene, or vitamin deficiencies.
Understanding these causes is the first step towards solving the problem. Treatments range from medication to dietary adjustments and proper oral care.
By understanding the causes and effective prevention strategies, you can protect your oral health. Read on for helpful tips.
Table of contents
What are Mouth Sores and Stomatitis?
Mouth sores and stomatitis are common issues that can cause discomfort and pain. Types of sores include blisters, cold sores, and chickenpox, each with different symptoms and causes.
Different Types of Sores
Mouth sores can vary greatly, often appearing as blisters, red areas, or white spots. Here are some common types:
1. Aphthous stomatitis: These are small, painful sores known as canker sores. They appear alone or in clusters and usually heal on their own within a couple of weeks.
2. Herpes simplex virus (cold sores): These sores are caused by a virus and typically appear on the lips but can also occur inside the mouth. They start as small blisters and develop into sores.
3. Candidiasis (oral thrush): A fungal infection causing white patches in the mouth or on the tongue, especially affecting those with weakened immune systems.
4. Lichen planus: A condition that leads to white, lacy lines and sometimes painful sores in the mouth.
5. Cancer-related sores: These can result from cancer or its treatment, especially after radiation therapy to the head and neck area.
6. Traumatic sores: Injuries from brushing too hard, biting the inside of the cheek, or from braces can cause these sores.
7. Sodium lauryl sulfate-related: Toothpaste containing this ingredient can cause or worsen mouth sores in some individuals.
Each type of sore has its own cause and often requires different treatment to heal properly and avoid infections.
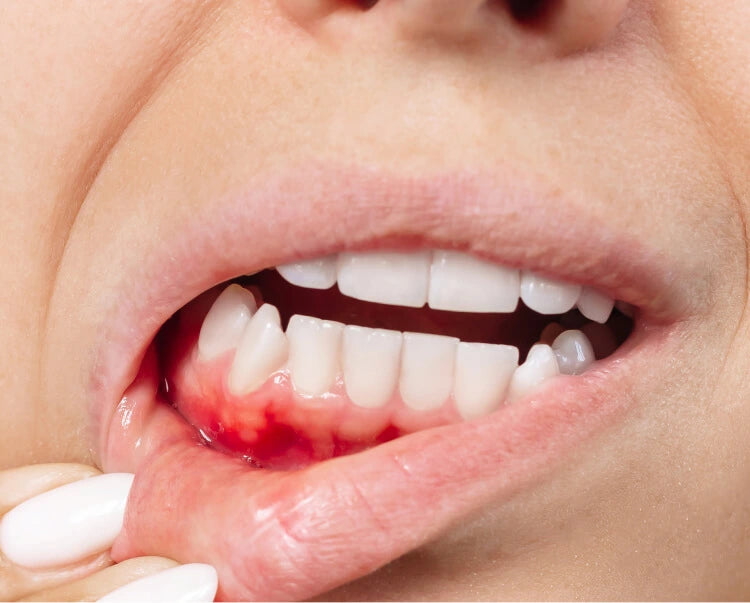
Causes
Infections play a major role in developing stomatitis. Poor oral hygiene, low saliva production, tobacco use, vitamin deficiencies, and side effects from certain medications can also lead to this condition.
Children often experience stomatitis due to viral infections, oral thrush, and aphthous stomatitis, presenting as white sores in the mouth or on the tongue.
Diseases like AIDS, benign mucous membrane pemphigoid, and lupus erythematosus can cause stomatitis. Stress, smoking, and lifestyle factors like a poor diet can also contribute to the problem.
Identifying the cause is crucial for effectively treating stomatitis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of stomatitis vary but often include blisters, sores, redness, and white patches in the mouth. Some people also experience coatings on their tongue. These signs can indicate various conditions, from mild infections to more serious viral diseases.
Both children and adults can be affected, and the symptoms can appear quickly and be painful.
Stomatitis often results from infections, poor oral hygiene, or vitamin deficiencies. Tobacco use and medication side effects can also play a role. It's important to recognize these symptoms so you can quickly seek treatment and find the best way to care for your mouth.
Treatment of Mouth Sores and Inflammation
Treating mouth sores and inflammation is important for alleviating discomfort. Mouthwashes and pain relievers can be used to ease pain and reduce inflammation. Oral care, including regular brushing and rinsing, is essential for promoting healing and preventing further infections.
Medical Treatment
Medical treatment for mouth sores and inflammation can include antifungals, antibiotics, and corticosteroids. Antifungals for topical use are crucial for keeping the mouth healthy and should always be used as prescribed.
Antibiotics may be necessary for bacterial infections in the mouth, while corticosteroids in tablet form can be used to treat a variety of conditions.
Radiation therapy to the head and neck area can cause mouth sores that require medical treatment to prevent infection. Topical NSAIDs can relieve pain, tenderness, and swelling in the mouth lining.
Dry mouth can be managed with sugar-free gum, lozenges, or drops, which are vital for oral health.
Dietary Adjustments
When dealing with mouth sores or inflammation, it's important to adjust your diet to avoid irritation and discomfort. Here are some tips for modifying your food and drink intake:
1. Avoid spicy foods, citrus fruits, vinegar, and salt, as these can exacerbate pain.
2. Choose soft and cool foods like yogurt, gelatin, or smoothies that won't irritate the sores.
3. Drink through a straw to avoid contact with the sore areas in your mouth.
4. Avoid alcoholic beverages and hot drinks, as these can delay the healing process.
5. Cut solid foods into small pieces to minimize chewing and reduce the risk of further injury.
6. Ensure adequate fluid intake to keep the mouth moist and promote healing.
By adjusting your diet in this way, you can help relieve the pain associated with mouth sores and promote a quicker healing process.
Oral Care
Oral care is essential for maintaining good oral hygiene and preventing mouth sores. Here are some important steps you can follow to ensure optimal oral care:
1. Brush your teeth thoroughly twice a day with a toothpaste free from sodium lauryl sulfate to reduce the risk of outbreaks.
2. Rinse your mouth regularly with an alcohol-free mouthwash.
3. Avoid smoking and tobacco products, as they can worsen mouth sores and increase the risk of complications.
4. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
5. Avoid acidic or spicy foods and beverages, as they can irritate the oral mucosa and worsen pain from sores.
6. Pay attention to your diet and avoid foods that can trigger or worsen stomatitis.
By following these guidelines, you can maintain good oral hygiene and reduce the risk of developing mouth sores as well as promote healing when they are already present.
Prevention of stomatitis
Keep your oral hygiene at its best by brushing and cleaning your teeth regularly. Learn more about how you can protect yourself from stomatitis and avoid triggering factors. Read on for useful tips.
Hygiene
Good oral hygiene is a key solution to prevent stomatitis and sores. Using dental floss, toothpicks, and regular brushing can remove bacteria and food particles that can cause infections. Fluoride treatment can also strengthen tooth enamel and prevent cavities, which is essential for maintaining good oral hygiene.
Avoid Trigger Factors
To avoid trigger factors for stomatitis and sores, it's important to:
1. Stay away from tobacco smoke, as smoking can worsen the condition of the oral mucosa.
2. Avoid foods or drinks that are sharp, hot, or acidic, as these can irritate sores.
3. Be aware of any allergic reactions to certain foods and avoid them.
4. Maintain good oral hygiene and avoid trauma in the mouth by not biting nails or chewing on hairpins.
5. Check toothpaste and other oral care products for any allergens that can trigger mouth sores.
Always consult a healthcare professional for further advice and treatment of stomatitis and sores.
Dietary Adjustments
Dietary adjustments play a crucial role in the prevention and treatment of stomatitis. Avoiding acidic or sharp foods can reduce irritation of mouth sores.
Increasing intake of vitamins and minerals through diet can also strengthen the immune system. Frequent small meals and avoiding overly hot or cold foods can further alleviate symptoms of stomatitis.
Stress Management
Stress can worsen stomatitis, so it's important to implement stress management methods such as exercise, meditation, and deep breathing. Identifying and managing stress factors can help reduce the risk of mouth sores.
Consider participating in mental health programs to learn coping strategies and strengthen your ability to handle stress in everyday life. Remember, a healthy lifestyle with adequate rest is also crucial to reducing stress levels and keeping stomatitis under control.
Conclusion
Prevention is key. Oral hygiene should be top-notch, and trigger factors should be avoided. A tailored diet and effective stress management can also help minimize the risk of stomatitis and sores.
Remember to maintain good oral hygiene, avoid trigger factors, and adjust your diet to minimize the risk of developing mouth sores.
FAQ
What are the typical symptoms of stomatitis?
Stomatitis can manifest as white sores in the mouth, pain, and in both children and adults, it can include fever and general discomfort. It's important to know the symptoms for quick treatment.
How are mouth sores treated?
Treatment of mouth sores depends on the cause. Mild stomatitis can be treated at home with mouthwashes, while more severe cases, like herpes labialis or thrush, may require medical treatment.
Is stomatitis contagious?
Yes, certain forms of stomatitis, such as herpes labialis, are highly contagious. It's important to practice good hygiene and avoid direct contact if you or someone close has an active infection.
Are there specific causes of stomatitis to be aware of?
Various factors can lead to stomatitis, including viral infections like herpes zoster, bacterial infections, inflammatory conditions like gingivitis, as well as celiac disease or gluten intolerance.
How can I prevent mouth sores?
Good oral hygiene is essential for preventing mouth sores. Also, avoid known irritants like certain foods if you have allergies or intolerances. Regular dental visits help keep dental problems like cavities and periodontitis in check.
When should I seek professional help for mouth sores?
If mouth sores do not heal within two weeks, worsen, or if you experience severe pain, fever, or other concerning symptoms, you should contact a doctor or specialist dentist for advice and treatment.
How quickly do mouth sores heal?
Most small mouth sores, such as canker sores and minor lesions, typically heal within 7 to 14 days without the need for treatment. Good oral hygiene and avoiding irritating foods and drinks can help speed up the healing process.





